If you’re interested in low-code app development, then chances are you’ve heard of Microsoft PowerApps.
The suite of tools, which is part of the Microsoft Power Platform, has been gaining popularity in recent years as a fast and easy way for individuals and businesses to create custom applications.
Power Apps is a collection of cloud-based tools and services that enable users to build apps using drag-and-drop features and pre-built templates, with very little coding expertise required. These apps work on mobile devices and can be used to streamline business processes, automate workflows, and enhance productivity.
In this article, we’ll explore the capabilities of Microsoft Power Apps in detail and highlight some of its key features.
We’ll explain how the platform can be used to create custom applications using a model-driven approach that addresses your business needs.
Let’s get started!
What Is Power Apps?
Power Apps is a suite of tools for rapid application development provided by Microsoft’s Power Platform that turns non-technical users into competent app makers who can quickly build and share powerful low-code apps.
With this suite of apps, services, and data platforms, anyone can become rapidly develop custom applications tailored to your specific business requirements.
As a Microsoft Power Apps user, you can create automated workflows that connect your favorite apps, services, and data source and enable you to synchronize files, create interfaces, receive notifications, collect data, modify data, automate data processes, and more.
It integrates well with other Microsoft Power Platform applications, such as Power Automate, Power BI, and Power Pages, to enhance your overall experience.
Key features of Power Apps
Low-code development: Power Apps is designed for non-developers to create custom no-code applications without requiring extensive coding skills.
Integration with Microsoft services: It integrates seamlessly with Microsoft cloud services, such as SharePoint, Microsoft Dynamics 365, Power Automate, and Power BI, making it easier to build and connect data-driven applications.
Mobile-friendly: Power Apps is optimized for mobile devices, so you can easily build and deploy mobile-friendly applications for iOS, Android, and Windows devices.
Customizable templates: Power Apps includes customizable templates to help users get started quickly with their app development projects.
AI and machine learning: Like any modern software tool, the underlying data platform of Power Apps includes AI and machine learning capabilities to help users automate business applications, adapt apps, and make smarter decisions.
Cloud-based: Power Apps portals are cloud-based, which means users can access their applications from anywhere, anytime, and on a mobile device or PC.
With Power Apps, your organization can streamline the enterprise process, enhance application development, and ultimately, improve productivity and efficiency.
As you explore and utilize this platform, you’ll find numerous ways to customize your business apps to align with your organization’s specific needs.
In the next section, we’re going to look at the components of Power Apps, so keep reading to learn more about how Power Apps can help you build apps that streamline your business logic and drive growth.
What Are The Components of Power Apps?
Power Apps enables you to create apps using data from a variety of sources. It has a range of components that enable users to build powerful model-driven apps.
In this section, we will explore the various components of Power Apps and take a look at how each one contributes to the platform’s overall functionality.
The main components of Power Apps include:
Data Sources: This component enables users to connect to various external data sources, such as Excel spreadsheets, SharePoint lists, SQL server databases, and other on-premises data sources, to create data-driven applications.
Canvas apps: The Canvas apps component enables users to create highly customizable applications with drag-and-drop UI elements and a low-code programming environment.
Model-driven apps: This component provides pre-built templates and workflows that users can customize to develop apps that work with the Common Data Service.
Connectors: This component allows users to connect to custom connectors and external services, such as Twitter, Dropbox, OneDrive, Google Drive, Microsoft Teams, Office 365, Power BI, and SharePoint, to access business data from multiple sources.
Microsoft Dataverse: This component is a powerful relational database that allows users to store and manage environments within Power Apps, Power BI, and Microsoft Dynamics 365.
AI builder: This component provides AI and machine learning capabilities that enable users to automate business rules and make smarter data-driven decisions.
Portals: This component enables users to create external-facing websites or portals that allow external users to access Power Apps data and functionality.
Each of these components plays a critical role in enabling users to create custom Power Apps apps quickly and easily. In the next section, we look at how you can create Power Apps.
Let’s go!
How to Create Power Apps?
Business users interested in building user-friendly mobile applications to solve business challenges and automate processes approach it in two ways: using templates and starting from a blank canvas.
Using Templates
One way to start creating your own apps is by using a template from Power Apps or Teams.
Templates provide pre-built app structures that you can customize to suit your specific requirements.
They are a great starting point to accelerate app development and learn more about the platform’s features.
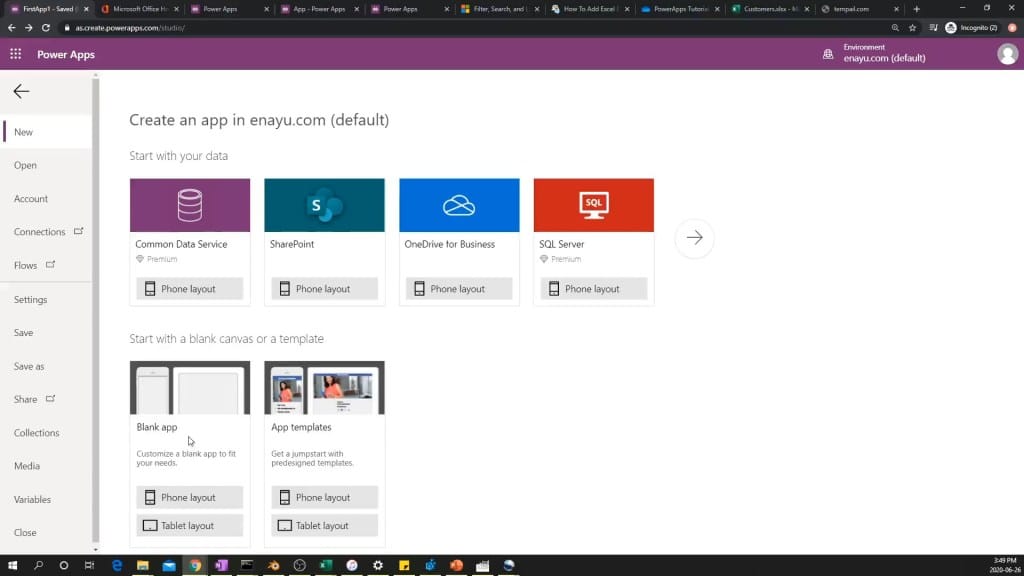
To access templates in Power Apps, navigate to the dashboard and click “Create” on the Power Apps menu. Browse through the available options and choose a template that is suitable for your business needs.
After selecting a template, you can modify it using Power Apps Studio, which makes creating apps feel more like building a slide deck in Microsoft PowerPoint.
But, what about doing things your own way and starting out fresh?
Starting With a Blank Canvas
If you prefer to build your app from scratch, starting with a blank canvas provides added flexibility and control.
Like templates, you can start a blank canvas app in Power Apps or directly within Microsoft Teams.
To create a blank canvas app in Power Apps, navigate to the dashboard and click “Create.” Choose “Canvas app from blank” and begin designing your app using Power Apps Studio, which features intuitive ribbons and menu structures similar to other Microsoft applications.
When starting from a blank canvas, consider the following elements to make your app visually appealing and functional:
Integrate your preferred data source to retrieve, store, and manipulate information.
Add positioning controls and components to create user interactions, such as Power Apps forms, qr codes, buttons, and galleries.
Customize the app layout and theme to reflect your branding and enhance usability.
Utilize formulas and expressions to add logic and functionality to your Power Apps app.
Explore different design possibilities and features to create custom business apps tailored to your specific needs.
Now that you know how to create model-driven apps using Power Apps, let’s take a look at how much a license costs.
How Much is Power Apps?
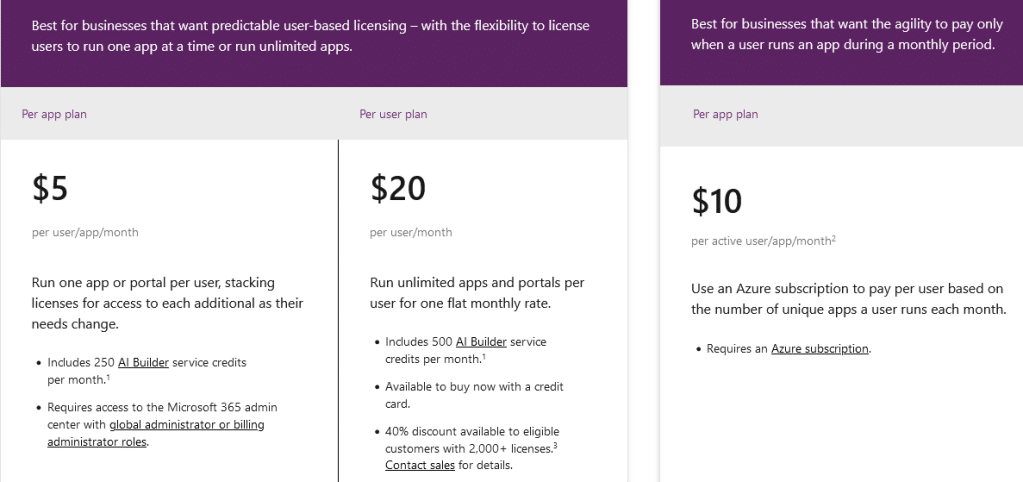
The different licensing options available for the Power Apps data platform. Source: Microsoft
Power Apps has a variety of plans available tailored to different needs.
1. Per app plan
First, there’s the per app plan, which costs $5 per user/app/month. This plan is ideal for businesses that want a predictable user-based licensing with the flexibility to stack additional licenses if their needs change.
2. Per user plan
The per user plan lets you run unlimited applications (within service limits) based on the full capabilities of Power Apps. It costs $20 per user/month.
This plan offers scalability and versatility for businesses that require multiple applications for their users.
3. Pay-as-you-go plan
There’s the Power Apps pay-as-you-go plan which allows individual users to run applications (1 app or 1 portal) without any licenses via an Azure subscription.
This plan provides flexibility for users who only need limited access to Power Apps.
Take the time to assess your business requirements, user needs, and budget constraints to choose the Power Apps plan that fits your organization best.
Next, we take a look at some popular use cases for Power Apps.
What Are The Real-World Uses For Power Apps?
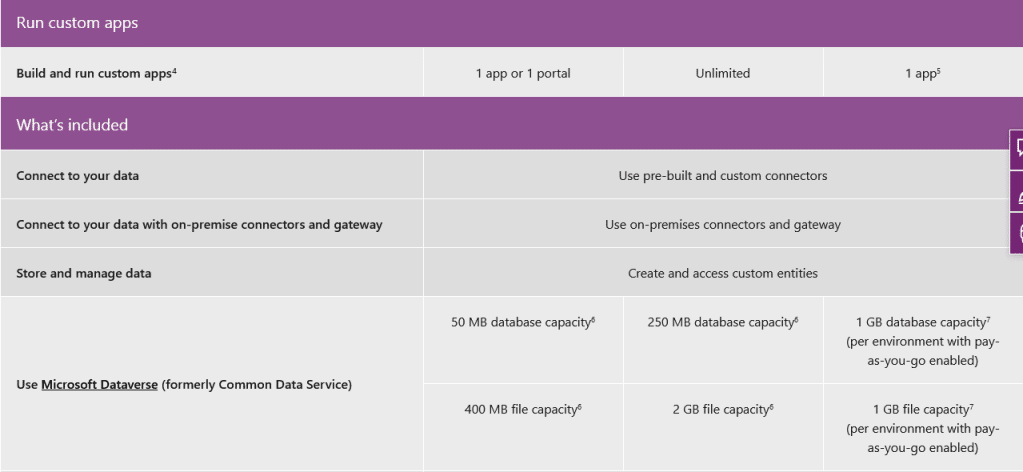
Some of the features are available in different Power App licenses. Source: Microsoft
Power Apps can simplify your life by automating mundane tasks and streamlining your workflow.
With Power Apps, the sky’s the limit when it comes to use cases! Here are just a few examples to get you started:
Data entry: Power Apps can save you hours of data entry time by allowing you to create apps that automatically populate data into spreadsheets, databases, or other data platforms.
Scheduling: Say goodbye to the back-and-forth emails when trying to schedule meetings. Power Apps can help you create a scheduling app that simplifies the process for everyone involved.
Inventory management: If you’re tired of manual inventory tracking, Power Apps can help you create a custom app that keeps track of your inventory levels and alerts you when supplies are running low.
Project management: With Power Apps, you can create an app that tracks project progress, deadlines, and team members’ tasks. Such lightweight apps can help keep everyone on the same page and ensure that projects stay on schedule.
HR: Power Apps can be used to track employee productivity, user roles, manage employee requests, and even facilitate the hiring process.
Customer relationship management (CRM): Using Power Apps, you can create a CRM app that helps your sales team manage leads, track deals, and keep in touch with customers.
The possibilities with Power Apps are endless. Whether you’re a business owner, a project manager, or an individual looking to streamline your personal workflow, Power Apps can help you get there.
The best part, Power Apps can be easy to learn and enjoyable too.
The Bottom Line
We’ve covered a lot of ground when it comes to Power Apps. We started by discussing what Power Apps is and how it can benefit you.
We then delved into the components of the data platform, including the various connectors, Canvas apps, controls, and data sources available.
We also looked at the pricing options on the Power Apps website and explored some of the best use cases for Power Apps, including workflow automation, data entry, scheduling, inventory management, project management, HR, and CRM.
With Power Apps, you can streamline your workflow, automate tasks, and save time and energy. The Power Platform empowers everyone, regardless of technical background, to build custom apps that can revolutionize the way they work.
Power Apps can be a game-changer for individuals and businesses alike. So, take the leap and start exploring the possibilities with Power Apps apps.
Who knows, you might just discover a new way to work smarter, not harder!
To learn more about how to get started with Power Apps, check out the tutorial below: