In the past, businesses were run based on what you know and who you know.
That is still true today.
However, thanks to technological advances, the ways we gain knowledge and create contacts have become lightning-fast. Corporate success hinges on leveraging data swiftly and accurately.
Power BI can transform the way organizations make decisions by giving them access to real-time information and enabling them to identify trends and patterns quickly.
To implement Power BI in your business:
- Assess your needs
- Get the right subscription
- Set up Power BI
- Clean your data
- Create reports and dashboards
- Collaborate and share
- Review and iterate
In this article, we’ll guide you through the process of integrating Power BI into your business, step by step.
You’ll also learn how to unlock the full potential of Power BI and maximize its benefits for your organization.
So, let’s dive in and get your business ready to harness the power of data with Power BI!
7 Steps to Implement Power BI in Your Business
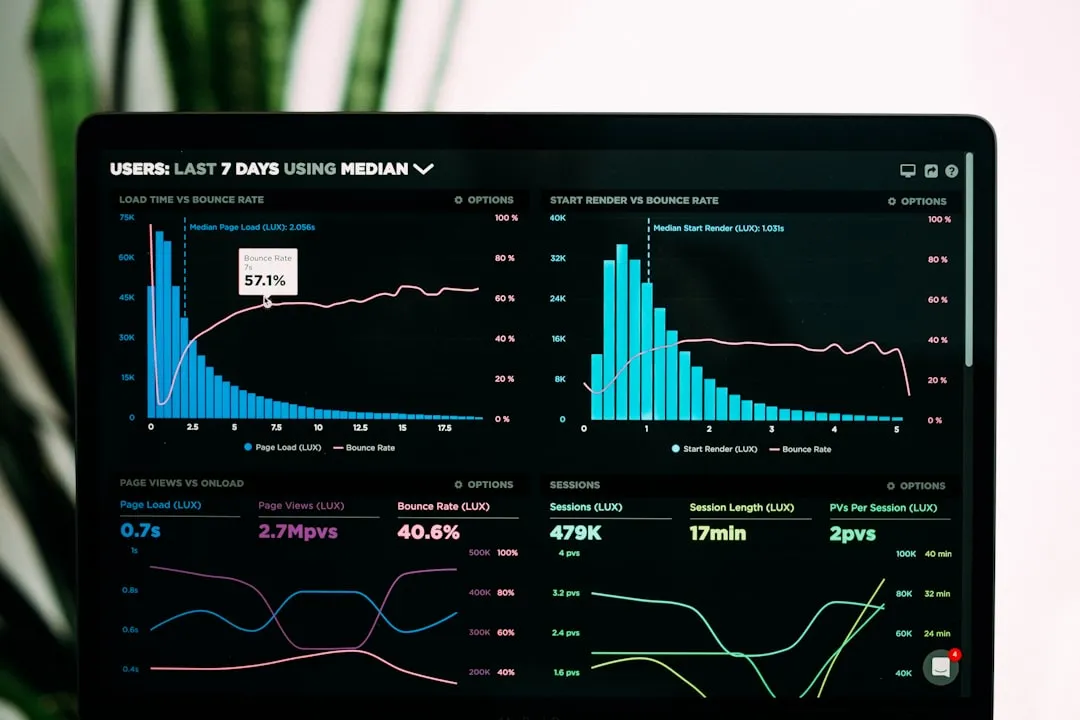
In this section, we’ll go over a step-by-step guide to implementing Power BI in your business. Each step is crucial to your success with Power BI, so make sure to follow them all carefully.
Step 1: Assess Your Needs
The first step in implementing Power BI in your business is to identify your data requirements. You’ll need to determine the sources of data you want to connect with and the specific insights you want to extract from that data.
You should answer questions like:
- What are my business objectives?
- What data sources do I need to connect with to meet these objectives?
- What specific KPIs do I want to track?
By conducting this initial assessment, you’ll have a clearer understanding of the data sources you need to connect to and the type of reports and dashboards you need to create to meet your business needs.
Step 2: Get the Right Subscription
After you’ve identified your data requirements, you’ll need to choose the right Power BI subscription plan. Power BI offers several subscription options, including a free plan and paid plans.
The free plan offers basic features and limited data storage, making it suitable for individuals or small businesses with minimal data requirements.
However, for more robust analytics, you might want to consider one of the paid plans, such as Power BI Pro or Power BI Premium.
- Power BI Pro: This plan is ideal for small to medium-sized businesses. It offers additional features, such as more storage, advanced sharing options, and data refresh rates, compared to the free plan.
- Power BI Premium: This plan is designed for large organizations with complex data requirements. It provides dedicated capacity, increased performance, and enhanced security features.
Choose the plan that best fits your organization’s needs and budget. Keep in mind that you can always upgrade your plan as your business grows, and your data requirements become more demanding.

Step 3: Set Up Power BI
Once you’ve chosen the right subscription plan for your business, you can begin the process of setting up Power BI.
To do this, you’ll need to follow these steps:
- Go to the Power BI website and sign up for an account if you don’t have one.
- After creating an account, sign in to Power BI.
- Once signed in, you’ll be directed to the Power BI service, where you can start creating and sharing reports and dashboards.
Step 4: Clean Your Data
Data preparation is a crucial step in the Power BI implementation process. Before you can start creating visualizations and dashboards, you’ll need to clean and transform your data to ensure its accuracy and reliability.
To clean and transform your data, you can use the built-in Power Query Editor, which allows you to:
- Connect to various data sources: Import data from multiple sources, such as Excel, SQL Server, Google Analytics, and more.
- Clean and transform data: Identify and correct any errors or inconsistencies in your data, such as missing values, duplicate entries, or incorrect formatting.
- Create data models: Organize your data into tables and establish relationships between different data sets.
By cleaning and transforming your data, you can be confident that your reports and dashboards will provide accurate and actionable insights for your business.
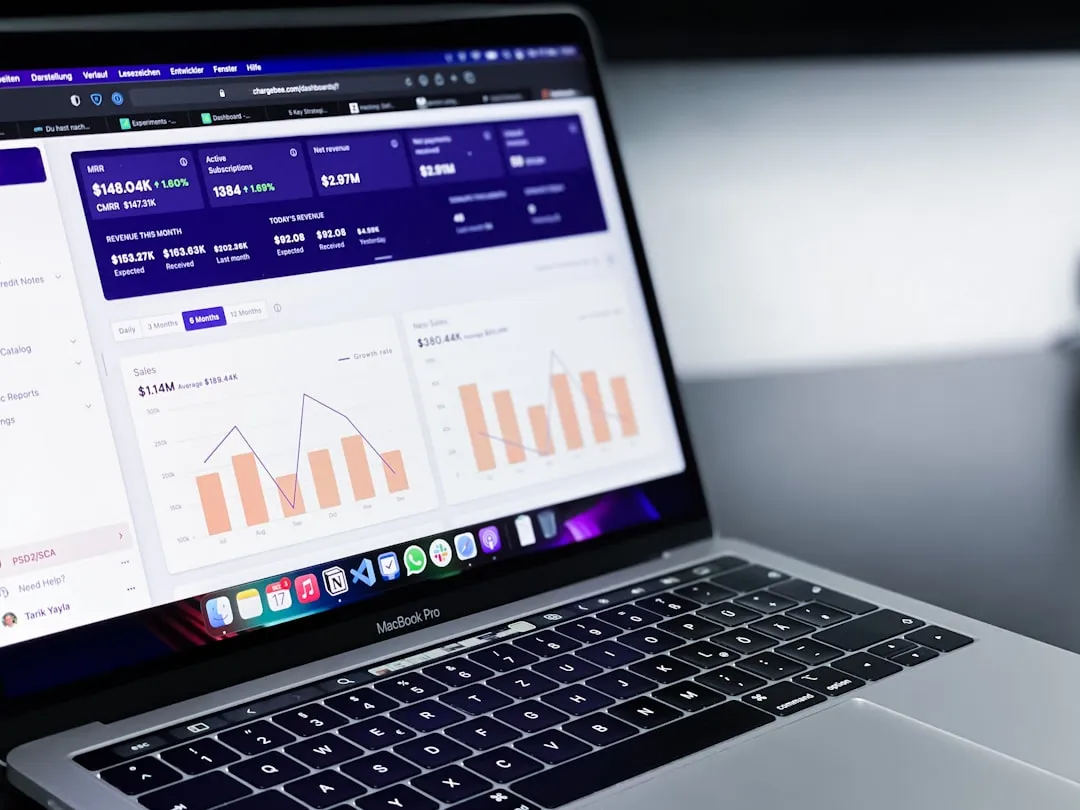
Step 5: Create Reports and Dashboards
Now that your data is cleaned and ready for analysis, you can start creating reports and dashboards.
In Power BI, you can create reports by selecting the data you want to analyze and choosing the type of visualization that best represents that data.
Some common types of visualizations include:
- Bar charts: To compare data across categories.
- Line charts: To track data trends over time.
- Pie charts: To show the proportion of a whole.
- Tables: To display raw data in a structured format.
- Maps: To visualize geographical data.
Once you have created reports, you can combine them into dashboards. Dashboards allow you to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) and track the overall health of your business at a glance.
To create a dashboard, simply pin the visualizations from your reports to a new dashboard. You can customize the layout and refresh intervals to suit your needs.
Step 6: Collaborate and Share
One of the key benefits of Power BI is its ability to facilitate collaboration and data sharing within your organization.
You can use the Power BI service to share reports and dashboards with colleagues and stakeholders.
To share a report or dashboard, follow these steps:
- Publish your report or dashboard to the Power BI service.
- Select the item you want to share in the navigation pane.
- Click on the “Share” button.
- Enter the email addresses of the recipients.
- Optionally, include a personalized message.
- Click “Send”.
By sharing your reports and dashboards, you can ensure that your team is always aligned and making decisions based on the most up-to-date information available.
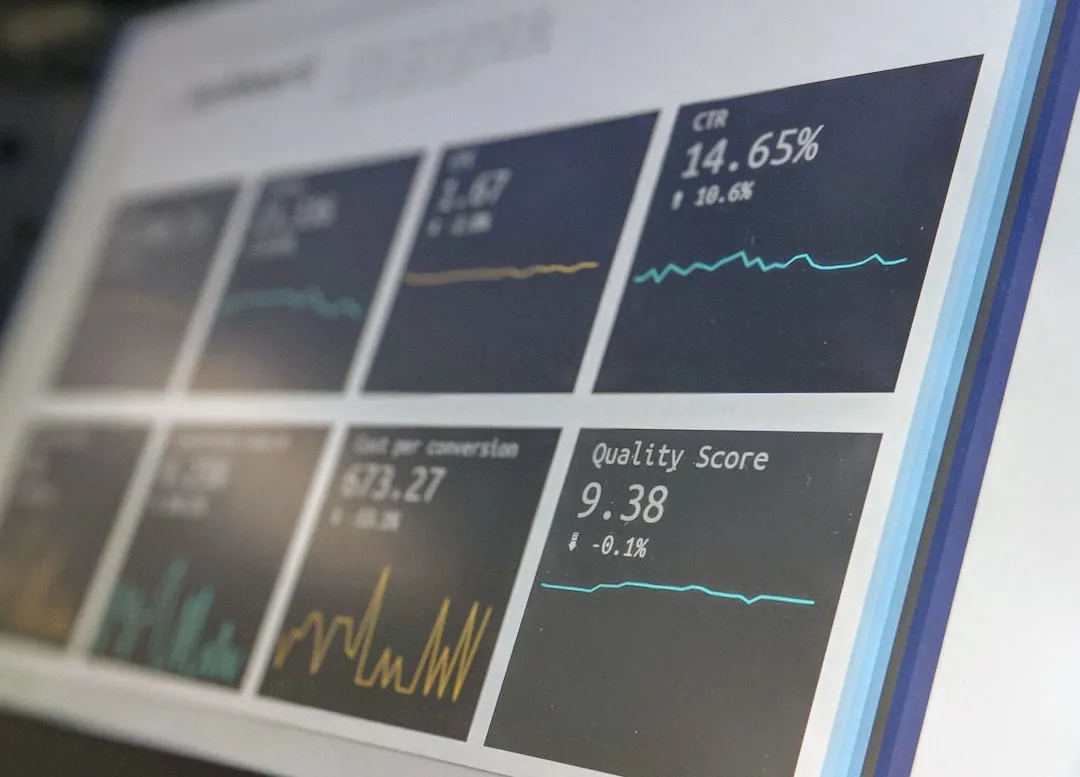
Step 7: Review and Iterate
As you start using Power BI, it’s essential to regularly review the reports and dashboards you’ve created and iterate on them as needed.
Set aside time for data review and report updates. During these sessions, analyze the performance of your business based on the insights provided by Power BI.
Look for areas of improvement and make adjustments to your reports and dashboards accordingly.
Also, be open to feedback from your team and stakeholders. They may have valuable insights that can help you refine your reports and make them even more valuable for your organization.
By regularly reviewing and iterating on your reports, you can ensure that your data analysis remains accurate, relevant, and aligned with your business goals.
So, now you’ve got the gist of things… why bother implementing Power BI?
Well, there are 3 strong reasons.
3 Benefits of Implementing Power BI in Your Business
By now, you’ve probably gathered that Power BI can bring a lot of value to your business. But just to drive the point home, here are 3 key benefits of implementing Power BI in your organization.
1. Gain Valuable Insights From Your Data
Power BI is a robust data analytics tool that allows you to gather and analyze data from various sources. By using this tool, you can unlock valuable insights that can help you make better-informed decisions.
2. Make Better-Informed Decisions
With Power BI, you can quickly and easily create dynamic reports and dashboards that can be shared with stakeholders across your organization.
This allows you to make better-informed decisions based on real-time data, rather than relying on outdated or incomplete information.
3. Save Time and Money
Using Power BI can significantly reduce the time and resources required for data analysis. It automates many of the manual processes involved in data analysis, allowing you to focus on interpreting the results and taking action.
Final Thoughts

As you can see, implementing Power BI in your business is a powerful step towards data-driven decision-making.
By harnessing the capabilities of Power BI, you can gain valuable insights from your data, make better-informed decisions, and save time and money in the process.
So, don’t wait any longer. Start your Power BI implementation today and unlock the full potential of your business data!
Are you looking for more advanced Power BI tutorials? Then check out our latest video:
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, you’ll find some frequently asked questions you may have when implementing Power BI in your business.
What are the steps to implement Power BI in an organization?
- Determine business goals and KPIs.
- Assess data sources and requirements.
- Choose the right Power BI subscription.
- Set up Power BI accounts and data connections.
- Clean and transform data.
- Create visualizations, reports, and dashboards.
- Share and collaborate on insights.
- Monitor and review reports regularly.
How to use Power BI in a small business?
To use Power BI in a small business, start with the free version to assess its value. Then, connect data sources, clean and transform data, create visualizations, and share insights with colleagues.
How to get started with Power BI?
To get started with Power BI, sign up for an account, download the Power BI Desktop application, and begin connecting to data sources. Then, use the Power Query Editor to clean and transform your data, create visualizations, and share insights.
What are the key steps to create a Power BI report?
- Import and clean data.
- Create visualizations (tables, charts, etc.)
- Add filters, slicers, and drill-downs.
- Arrange visualizations on the report canvas.
- Add a title and other relevant text.
- Customize the report’s appearance.
- Publish and share the report.
What is the best way to implement a Power BI strategy?
- Identify key business objectives and KPIs.
- Assess data sources and availability.
- Create a data model to support business requirements.
- Build a series of reports and dashboards to address objectives.
- Share insights and foster a data-driven culture.
- Regularly review and iterate on reports.
How can a company get Power BI certification?
To get Power BI certification, consider the Microsoft Certified: Data Analyst Associate. This certification covers Power BI, data analysis, and DAX. Prepare for the exam with study materials and practice tests.