In a world where technology continues to amaze us, you might have heard the term “AI agent” floating around. But what exactly does it mean?
An AI agent is like a digital helper that can think and make decisions on its own. It uses information from its surroundings, learns from its experiences, and acts to accomplish tasks without human intervention.
Read on to learn and understand this fascinating digital companion and how it’s shaping our lives.
So, let’s dive in and unlock the secrets of AI agents!
(Running low on time to read this article? Scroll down to see the video version)
Understanding AI Agents
AI agents are software programs or systems that are designed to perceive their environment, make decisions, and take actions autonomously to achieve specific goals.
These AI systems can be used in various applications such as chatbots, robotics, personal assistants, and more.
Key Aspects of AI Agents
Here are some of the key aspects of these intelligent agents:
- Learning and Adaptation: Guided by their agent program, they are capable of learning from their experiences and adapting to new situations.
They can improve their performance over time by processing and analyzing data. - Interaction with the Environment: They can interact with and affect their surroundings. They often have actuators or mechanisms that allow them to take physical actions, such as a robot manipulating objects or a self-driving car navigating roads.

- Learning from the Environment: Their understanding of the environment comes from using their sensors, such as cameras, microphones, or text inputs. These sensors enable them to collect data and perceive the state of the environment.
- Decision-Making: An AI agent works by making decisions based on the information they perceive and the knowledge they have acquired.
Driven by their agent function, they employ algorithms and reasoning processes to determine the best course of action to achieve their objectives.

- AI Agent Goals: Their role is defined by the goals you must achieve to fulfill a specific task or request.
These goals can range from simple tasks like scheduling appointments to complex tasks like financial decision-making or running optimization simulations. - Artificial General Intelligence (AGI): Another crucial component in the development of AI agents is reaching artificial general intelligence (AGI), which aims to build systems that possess the intelligence to understand, learn, and apply knowledge across various domains.
These aspects collectively define the fundamental capabilities of AI agents and enable them to perform a wide range of tasks in various applications.
Types of AI Agents
There are several types of AI agents, each with different approaches to solving problems and achieving goals.
The top 5 types include:
1. Simple Reflex Agents

These reactive agents are like quick responders. They make decisions based solely on the current input they receive. They are purely reactive and lack the capability to plan for the future or learn from past experiences.
For example, if a sensor detects an obstacle in front of a robot, a simple reflex agent might make it turn to avoid the obstacle without considering any broader context.
2. Model-Based Reflex Agents

Model-based agents maintain an internal model or representation of the world, allowing them to consider some context beyond just the current input.
This internal model helps them make slightly more informed decisions.
For instance, a model-based reflex agent might remember the location of obstacles it encountered earlier and plan its path accordingly.
3. Goal-Based Agents

Goal-based agents are like planners. They have specific objectives or goals they aim to achieve. These agents consider their current state, the goal they want to reach, and a set of actions to get there.
Think of it as setting a destination on your GPS—your intelligent agent will plan the best route to reach that goal.
4. Utility-Based Agents

Utility-based agents are the pragmatists of the artificial intelligence world. They not only have goals but also assign values or utilities to different outcomes. These utilities help them decide which action to take when there are multiple ways to achieve a goal.
It’s like choosing between taking a scenic route or a faster one based on your preferences.
5. Learning Agents

These machine learning agents are the most advanced and are the students of AI. These agents can adapt and improve their decision-making based on the data and feedback they receive.
They can be trained to recognize patterns, make predictions, and optimize their actions. For example, a learning agent might become a better chess player by analyzing past games and learning from wins and losses.
These different types of AI agents cater to various problem-solving scenarios and exhibit varying degrees of sophistication in their decision-making processes. Depending on the task at hand, one type of agent may be more suitable than another.
How Are AI Agents Being Used Today?
AI agents have rapidly integrated into various aspects of our lives and industries, bringing about significant advancements and improvements.
Here are some of the notable uses of AI agents:
- Virtual Assistants: AI-powered virtual assistants like Siri, Google Assistant, and Alexa help users with tasks such as setting reminders, answering questions, and controlling smart home devices.
- Software Industry: Agents play a crucial role in the software industry. As a software agent, they can streamline processes by handling tasks more efficiently than humans, saving time and resources.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars and autonomous drones use agents to perceive their surroundings, make driving decisions, and navigate safely. This technology is poised to revolutionize transportation.
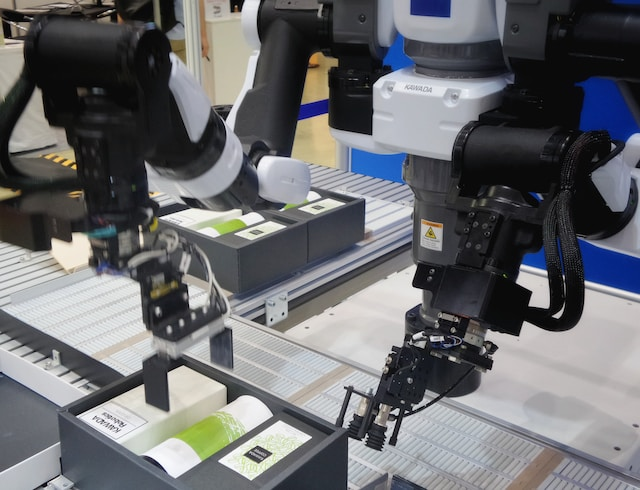

- Robotics: In manufacturing, AI agents control industrial robots to perform repetitive and precise tasks, such as assembling products, welding, or handling materials.
Collaborative robots (Cobots) work alongside humans, enhancing productivity and safety. - Healthcare: Agents assist healthcare professionals in diagnosing diseases, analyzing medical images (like X-rays and MRIs), and managing patient records.
They can also provide personalized health recommendations and monitor patient vitals. - Finance: In the financial industry, agents are used for algorithmic trading, fraud detection, and customer service chatbots.
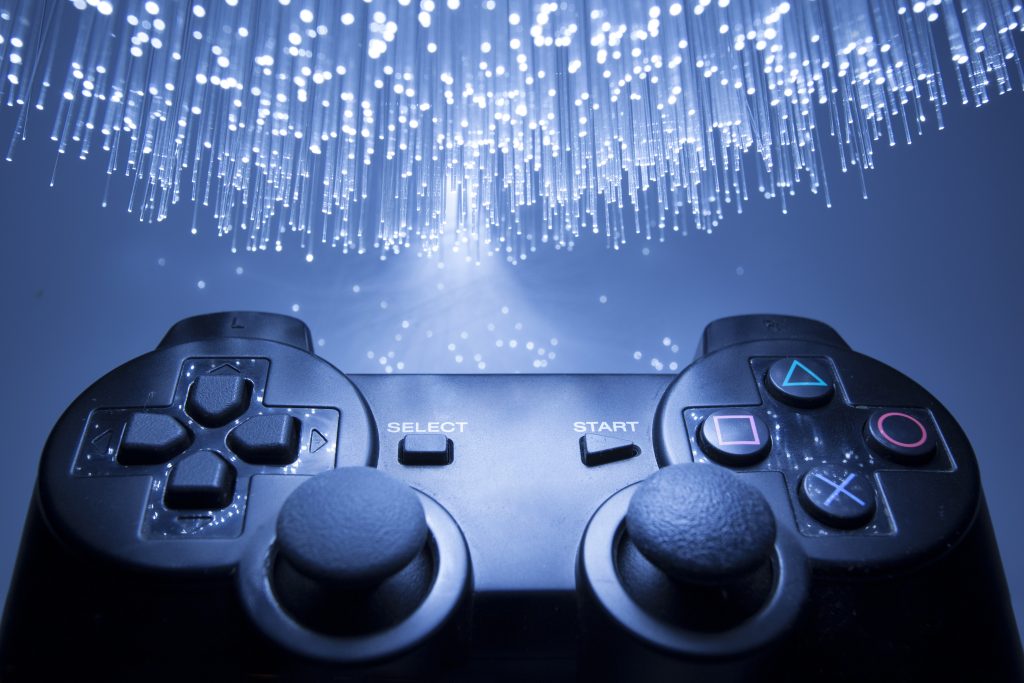
They can analyze vast amounts of data quickly, making them valuable for decision-making and risk assessment. - Gaming: Agents are integral to video games, where they control non-player characters (NPCs) and opponents. These agents can adapt to a player’s behavior and provide challenging and engaging gaming experiences.

- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Agents powered by NLP technology enable language translation, sentiment analysis, and chatbots that can hold realistic conversations with users, improving customer support and communication.
- Cybersecurity: Agents help detect and respond to security threats by analyzing network traffic patterns, identifying anomalies, and safeguarding systems against cyberattacks.
- Education: In education, agents offer personalized learning experiences, adapting content and pacing to individual students’ needs.
They can also provide immediate feedback and assessment.
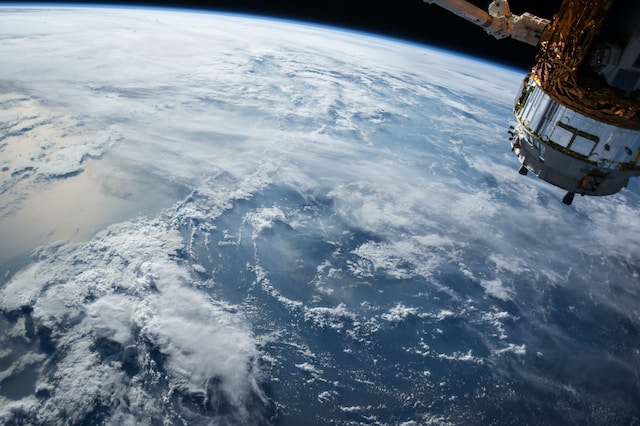

- Space Exploration: Agents assist in space exploration by autonomously controlling spacecraft, rovers, and satellites. They have the capability to make crucial decisions during missions to explore distant planets and celestial bodies.
These examples demonstrate the versatility and impact of AI agents across a wide range of fields. As technology continues to advance, we can expect agents to play an even larger role in shaping the future of various industries and improving everyday life.
Limitations of AI Agents
While AI agents have made remarkable strides, they are not without their limitations. Understanding these limitations is crucial for developing realistic expectations and addressing potential challenges:
- Lack of Common Sense: Agents lack a true understanding of the world. They may struggle with tasks that require common sense reasoning or contextual understanding, making them prone to errors in novel situations.
- Ethical Dilemmas in Decision-Making: Agents make decisions based on data and machine learning algorithms, which may inadvertently perpetuate biases present in the training data. This can result in unfair or discriminatory outcomes, particularly in areas like hiring or lending decisions.

- Limited Creativity: Agents excel at tasks involving patterns and rules but often struggle with creative thinking, innovation, or generating original ideas. They lack the ability to think “outside the box.”
- Data Dependency: Agents heavily rely on data for learning and decision-making. When confronted with data they haven’t encountered before or in low-data situations, their performance can suffer.
- Lack of Emotional Intelligence: Even rational agents do not possess emotional intelligence or empathy. They cannot understand or respond to human emotions, which limits their effectiveness in fields like mental health or counseling.
- Continuous Learning Challenges: While agents can learn from data, they often require extensive retraining to adapt to changing environments or tasks. This can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.

These limitations highlight the need for careful development and deployment of AI agents, along with ongoing research and ethical considerations to mitigate these challenges.
While agents excel in specific areas, they are not a panacea and must be used judiciously, especially in contexts where human judgment, common sense, and ethical decision-making are essential.
The Future of AI Agents
As AI technology continues to advance at an astonishing pace, the future of AI agents holds immense promise.
Here are the top five exciting developments we can anticipate:
- Advancements in AI Agent Technology: Agents will become even more intelligent and capable. Improved algorithms, better data, and enhanced hardware will empower AI agents to perform complex tasks with greater accuracy and efficiency.
- Advanced Language Models: Research into Large Language Models (LLMs) has already demonstrated significant advancements in understanding and generating human-like speech.
This development offers the potential for more sophisticated communication between agents and humans, elevating the capabilities of these agents. - Human-AI Collaboration: The future will see closer collaboration between humans and AI agents, for example, with Web3.
AI agents will assist and augment human capabilities in various fields, leading to new forms of productivity, creativity, and problem-solving.

- Ethical Frameworks and Regulations: As agents become more integrated into society, there will be a growing focus on ethical considerations and regulations.
Ensuring fairness, transparency, and accountability in AI agent behavior will be a top priority. - Personalization and Customization: Agents will become more personalized, adapting to individual preferences and needs. From virtual assistants that truly understand and anticipate user needs to personalized healthcare recommendations, AI will offer tailored experiences.
- Autonomous Systems and Industry Disruption: Industries such as transportation, healthcare, and finance will witness significant disruption as autonomous AI agents take on more autonomous roles.
Self-driving cars, AI-assisted surgery, and automated financial analysis are just the beginning of this transformation.
The future of AI agents promises a world where human-machine collaboration leads to unparalleled innovation and efficiency.
However, it also raises important questions about ethics, privacy, and the responsible development and use of AI.
As we journey into this future, careful consideration and guidance will be essential to ensure that AI agents benefit humanity while addressing their inherent challenges.
Final Thoughts
As we wrap up our journey, it’s clear that AI agents are here to stay, propelling us into a future where human-machine collaboration knows no bounds.
From virtual assistants simplifying our daily tasks to self-driving cars revolutionizing transportation, AI agents are transforming the way we live, work, and play.
But with great power comes great responsibility. The rise of agents brings forth critical questions about ethics, fairness, and the delicate balance between man and machine.
In this dynamic landscape, one thing is certain: the journey is far from over.
The world of AI agents is evolving, and its potential knows no limits.
So, let’s embrace this digital frontier with curiosity, wisdom, and the firm belief that together, humans and agents can shape a brighter, more intelligent future.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do AI agents differ from humans?
AI agents are autonomous programs or systems that perform tasks or make decisions simulating human-like intelligence.
They differ from a human agent in several ways. As a rational agent, they can process information and solve problems more rapidly than humans, without emotions, physical limitations, or inherent biases. However, agents usually lack the social and creative aspects that humans possess.
What are the key agent types in artificial intelligence?
There are several types of agents in artificial intelligence:
- Simple Reflex Agent
- Model-Based Reflex Agent
- Goal-Based Agent
- Utility-Based Agent
- Learning Agent
Each type has its strengths and limitations, designed to address specific problems or tasks.
How does a simple reflex agent function?
A simple reflex agent acts based on the current state of its environment and a set of predefined rules. It perceives the environment, evaluates rule conditions, and reacts accordingly.
However, simple reflex agents operating in a partial environment may make them more suitable for simple tasks rather than complex situations.
What is the role of goals in AI agents?
Goal-based agents focus on achieving specific objectives. They use their understanding of the environment and available actions to plan steps that help them achieve their goals.
These agents can adapt to changing situations and make decisions based on what best suits their aim, providing more flexibility compared to rule-based agents.
What is a utility-based agent’s purpose?
Utility-based agents aim to maximize their expected utility – a measure of the desirability of a particular outcome. They consider the potential outcomes of their actions, their probabilities, and their subjective utilities in order to make optimal decisions.
This approach allows them to make better choices than goal-based agents in complex environments with multiple competing goals or uncertainty.
Can you provide an example of a model-based agent?
A model-based agent uses a model of the environment to track the current state and predict future states.
For example, an intelligent traffic light controller could be a model-based agent. It would maintain a model of the traffic patterns, predict congestion based on historical data, and adapt the traffic signal timings to optimize the flow of vehicles.
This type of agent is capable of handling dynamic and uncertain environments more effectively than simple reflex agents.