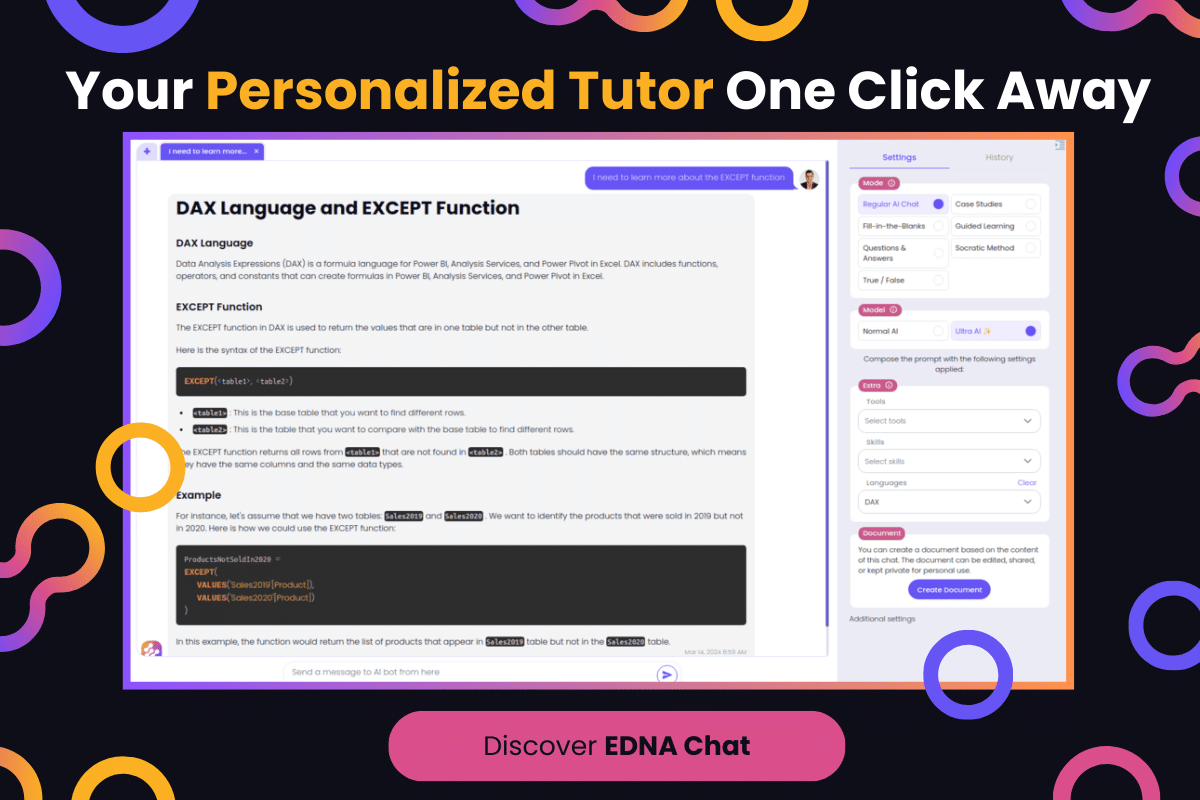
Introduction to Web Automation and Python
Web automation involves using scripts to interact with websites, automating repetitive tasks. This is particularly useful for tasks like logging into websites, filling out forms, data scraping, etc. Python is a common language for web automation due to its simplicity and the robustness of its libraries.
Prerequisites
Download the WebDriver for your browser and place it in a directory that’s in your system’s PATH.
Setup Instructions
Install Required Libraries
Example: Automating Login to a Website
We’ll demonstrate how to automate logging into a website using Selenium.
Step-by-Step Guide
Complete Script
Here’s a full script encompassing all the steps discussed:
With this guide, you can automate the login process for a website using Python and Selenium, providing a basis for further automation tasks post-login.
Setting Up Your Environment and Tools
Step 1: Install Necessary Libraries
Firstly, we need to install the necessary libraries for our Python environment. These will include selenium for browser automation and webdriver-manager to easily install and manage browser drivers.
Step 2: Setting Up WebDriver
Download the browser driver you need for Selenium. Using the webdriver-manager simplifies this process:
Step 3: Automate Logging into a Website
Below is a Python script that automates logging into a website. For this example, we’re using a hypothetical website http://example.com.
Step 4: Handling Dynamic Website Elements
Websites often have elements that load dynamically, and Selenium needs to wait for these to appear. Use WebDriverWait and expected_conditions to handle such elements:
Step 5: Structuring Your Code
For maintainability, encapsulate the functionality in functions and possibly a class. Here’s an example of turning the above script into a class-based approach:
By breaking down tasks and encapsulating them in a class, you make it easier to maintain and extend your automation script.
Part #3: Handling Web Elements with Selenium
This section will cover interacting with web elements using Selenium with Python for process automation. By the end of this part, you should be able to automate tasks such as logging into websites and performing various post-login actions.
Import Required Libraries
Initialize WebDriver
Open the Target Website
Locate Web Elements
Locating elements by ID, name, CSS selector, and XPath.
Interact with Web Elements
Interact with the web elements to log in.
Post-Login Actions
Wait for the new page to load and then perform additional actions.
Extract Information
Extract information from the web page after logging in.
Clean Up
Close the browser once the task is completed.
Full Script
With this implementation, you should be able to automate logging into a website and perform various post-login tasks using Selenium with Python.
Securely Managing Credentials in Python
When automating the process of logging into websites, securely managing credentials is crucial to prevent sensitive data exposure. Below is a practical implementation using environment variables to securely manage credentials.
Using Environment Variables
Environment variables are a secure way to store and retrieve sensitive information such as usernames and passwords. Below are the steps for managing credentials using environment variables in a Python script.
Step 1: Set Environment Variables
Before running the script, set the environment variables in your operating system. For example:
On Windows:
On macOS/Linux:
Step 2: Create a Python Script to Retrieve and Use Credentials
Here’s how you can retrieve these environment variables within your Python script.
Explanation
os.getenv to retrieve the username and password stored in environment variables.driver.get(url).By following this implementation, you can securely manage and use credentials in your Python automation scripts.
Automating Login Processes with Python and Selenium
Below is a clear, practical implementation of a script that automates logging into a website using Python and Selenium.
Code Implementation
Notes
Required Modules:
pip install selenium.pip install webdriver-manager.Element Identifiers:
"login_field", "password", and "logout_button" with the actual ID attributes from the webpage you’re automating.By methods accordingly, e.g., By.NAME, By.CLASS_NAME.Exception Handling:
TimeoutException is caught to handle scenarios where the login page or subsequent elements take too long to load.Post-Login Tasks:
Security:
This implementation provides a robust starting point for automating login processes using Selenium in Python. Adapt the element locators and post-login actions based on the specific requirements and structure of the target website.
Post-Login Task Automation
Overview
The following script demonstrates how to automate post-login tasks on a website using Python with the Selenium library. This example assumes you have already logged into the website and are looking to perform additional actions such as navigating to a specific page, filling out a form, or extracting data.
Implementation
Explanation
Initialize the WebDriver: This uses the Chrome WebDriver to control browser automation.
Navigate to the Website: This takes the user to a specific page after login (e.g., /dashboard).
Navigate to Profile: Clicks the “Profile” link to navigate to the user’s profile page.
Fill Out a Form: Finds the form fields for the address and city, clears them if necessary, inputs new data, and submits the form.
Extract Data: Fetches specific information (e.g., account balance) from the webpage and prints it.
Handling Cleanup: Ensures to quit the WebDriver to close the browser properly.
Note
By.ID, By.LINK_TEXT) based on the actual HTML structure of the target website.time.sleep() for simplicity.This script provides a practical basis for automating post-login tasks once the initial login phase has been successfully completed.
Unit 7: Error Handling and Debugging in Web Automation with Python
Error handling and debugging are critical skills to ensure that your web automation scripts are robust and reliable. This section covers practical implementations for error handling and debugging while automating web tasks using Python with Selenium.
1. Importing Necessary Libraries
2. Setting Up Logging
3. Implementing Error Handling
Example Function: Logging into a Website
4. Using the Function in a Script
5. Debugging Tips
-
-
-
- Verbose Logging: Ensure that your logging captures enough information to trace issues.
- Breakpoints: Use breakpoints in your IDE to step through the script.
- Exception Details: Always log exception details with stack traces for better diagnostics.
- Screenshots: Capture screenshots on exceptions to visualize the issue.
-
-
Conclusion
By incorporating robust error handling and detailed logging, you can make your web automation scripts more reliable and easier to debug. These practices help you quickly identify and address issues that arise during the automation process. Implement the above examples in your automation scripts to enhance stability and maintainability.
Best Practices and Advanced Techniques in Web Automation with Python
To build robust, maintainable, and secure scripts for web automation, it is essential to integrate best practices and advanced techniques into your Python code. Below are key implementation points for unit #8 of your project:
Using Page Object Model (POM)
The Page Object Model is a design pattern that enhances test maintenance and reduces code duplication. Here’s an example implementation:
Folder Structure
login_page.py
dashboard_page.py
test_login.py
Using Fixtures for Setup and Teardown
Leveraging fixtures when using frameworks like pytest makes your code cleaner and more reusable.
Data-Driven Testing
To ensure broad coverage with different sets of input data, integrate data-driven tests using pytest‘s parameterization.
Advanced JS Interactions and AJAX Handling
In certain automation scenarios, you may need to interact with dynamic elements or wait for AJAX requests to complete.
Advanced Task Automation Example
Integrating Advanced Task in Tests
By applying these best practices and advanced techniques, you ensure your automation scripts are efficient, maintainable, and robust. This will enable seamless scaling and adaptability to future changes in the application under test.